- (888) 55-SOLAR
- [email protected]
solargardens
February 28, 2024
February Temperatures Hit All Time Highs: Climate Change Concerns
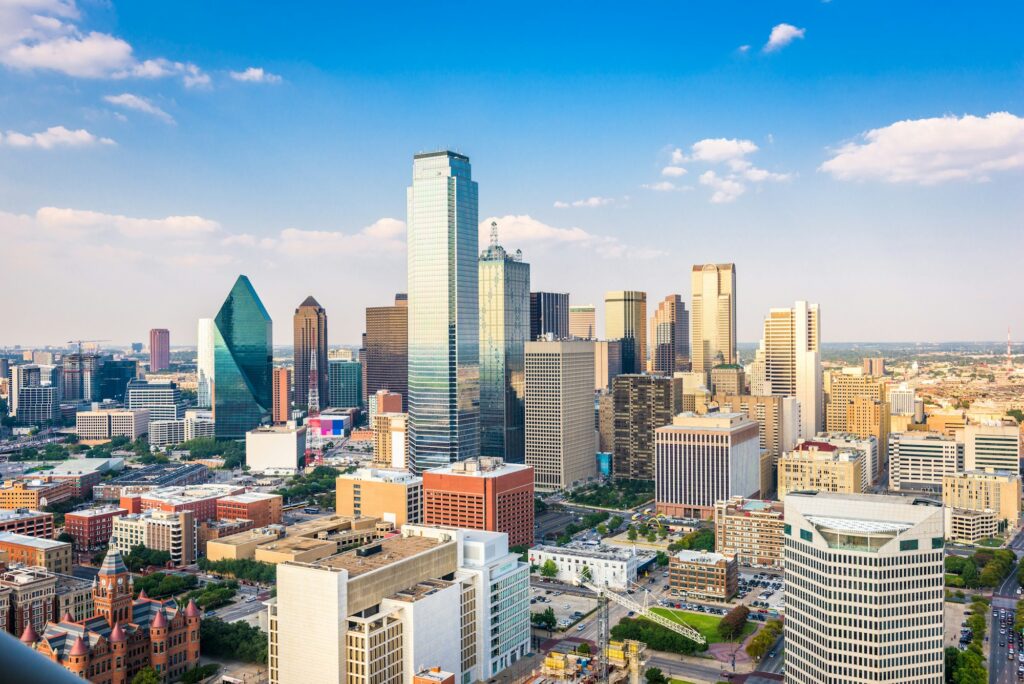
Cities across the United States have experienced record-breaking heat this February, raising eyebrows and climate change concerns alike. While winter is typically a time for snow and cold, these unseasonable temperatures prompt a deeper examination.
Record Breaking Heat In February
In an era where climate anomalies have become the norm rather than the exception, the United States is experiencing symptoms of a climatic shift. This February, a month traditionally synonymous with chill and frost, has painted a different picture altogether.
Cities from coast to coast have recorded temperatures that aren’t just above average—they are unprecedented.
But these aren’t isolated incidents or mere statistical flukes. They are symptomatic of a larger, more concerning trend. Such statistics are clear signals of the accelerating pace of global climate change.
Climate Change: How It Affects The Weather and Environment
To understand the connection between the recent weather phenomena and broader climatic shifts, it’s essential to delve into the fundamentals of climate change and its impact on weather patterns.
Climate change refers to significant changes in global temperatures and weather patterns over time. While climate variability is not new, the rapid changes currently being observed are predominantly due to human activities, notably the burning of fossil fuels, which release large amounts of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane into the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to a warming effect known as the greenhouse effect.
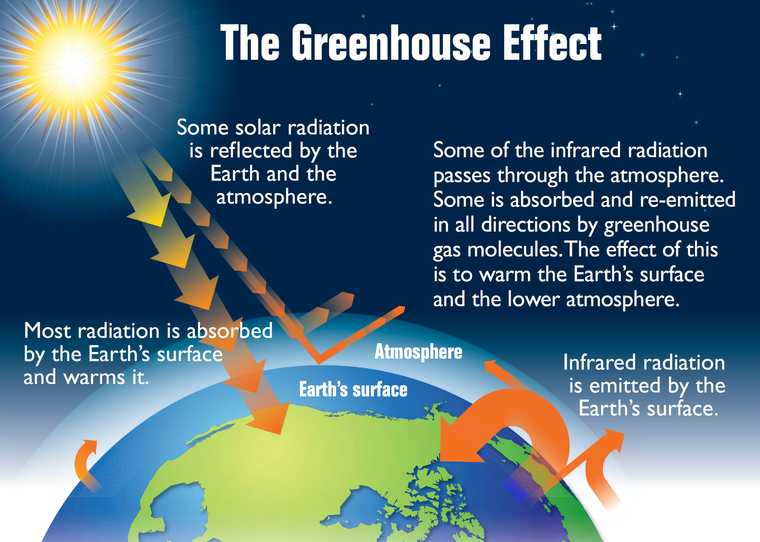
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the global average surface temperature has risen by about 1.1 degrees Celsius (2 degrees Fahrenheit) since the late 19th century. This increase in temperature has accelerated in recent decades, directly correlating with the rise in greenhouse gas emissions from human activities.
This warming has profound impacts on weather patterns, making extreme weather events more frequent and intense.
In general, warmer global temperatures contribute to a more dynamic atmosphere, leading to more severe storms, heat waves, droughts, and cold spells. Specifically, as the average global temperature increases, so does the probability of extreme weather events.
Furthermore, the warming of the planet impacts the polar jet stream, a band of strong winds in the upper levels of the atmosphere that play a crucial role in determining the weather in the mid-latitudes. The warming of the Arctic, which is occurring at a rate more than twice the global average, weakens the jet stream, causing it to meander and stall. This can lead to prolonged weather conditions, such as unpredictable heatwaves or cold spells, as experienced in the United States and around the world.

Global Impacts Of Unusual Weather Patterns
The unusual weather patterns and record-breaking temperatures observed in the United States serve as a microcosm of a global phenomenon driven by climate change. This global shift is not confined to any single region; it is a worldwide crisis with far-reaching implications that transcend national borders and socio-economic divisions.
Environmental Consequences
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) project that global temperatures will continue to rise if greenhouse gas emissions are not significantly reduced. This could lead to a global temperature increase of 1.5 to 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels within the next few decades, crossing a threshold that scientists believe will bring about even more severe and irreversible climate impacts.
Economic Impact
The economic ramifications of climate change are influencing every sector of the global economy and affecting the livelihoods of billions of people.
- Agricultural sectors worldwide are facing unpredictability, affecting food security and livelihoods, especially in developing countries reliant on farming.
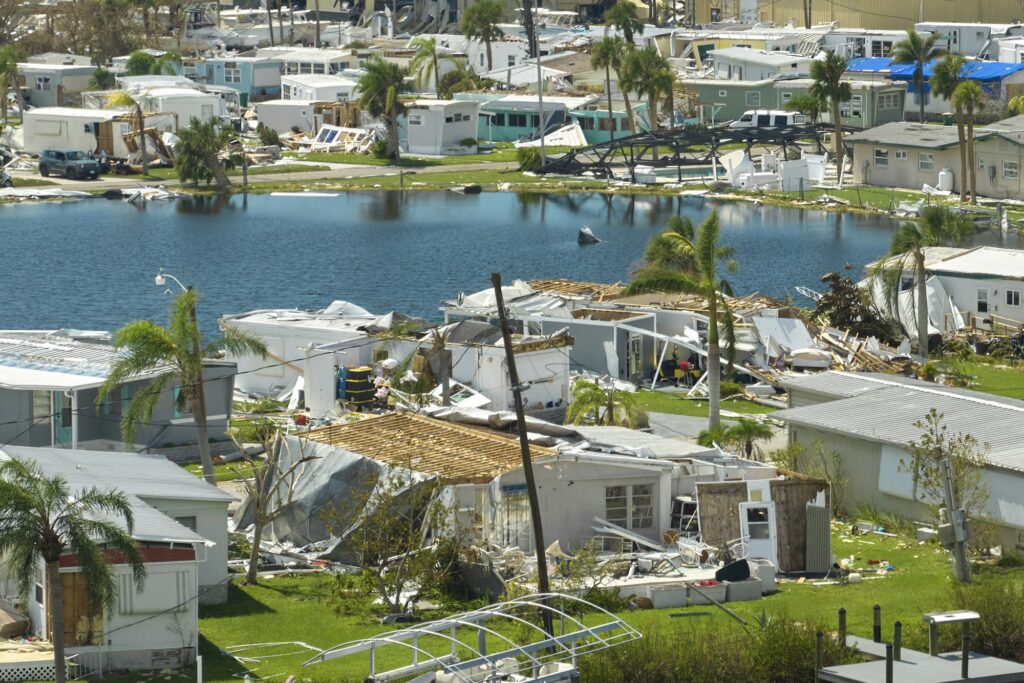
- The insurance industry is facing mounting challenges as the frequency and severity of natural disasters continue to rise.
- Energy sectors face fluctuations in energy demands and production with an increased need for alternative renewable energy sources.
Beyond immediate impacts, climate change poses a long-term threat to global economic growth. The cumulative cost of climate-related disasters, combined with the need for substantial investment in adaptation and mitigation strategies, can alter economic development.
Health Risks
The health implications of climate change are becoming increasingly apparent as air quality continues to worsen. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it’s been reported that about 99% of the global population breathes air that exceeds WHO guideline limits containing high levels of pollutants. The results in increased risk for chronic respiratory conditions such as asthma and COPD.
Social & Political Tensions
As natural resources become scarcer and environmental conditions deteriorate, social and political tensions are likely to escalate. Competition for water, food, and land can lead to conflicts and accelerate existing inequalities and injustices, leading to social unrest and geopolitical tensions.

Global Response & Social Cooperation
Addressing the global implications of climate change requires international cooperation and concerted efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate impacts. However, meeting these challenges necessitates not only government action but also private sector involvement and individual commitment.
The Paris Agreement is an example of an international agreement that requires nations to submit and regularly update their national determined contributions (NDCs), outlining their plans to reduce emissions and adapt to climate impacts.
Our goal at Solar Gardens is to invite everyone to rethink our relationship with the environment, with each other, and with future generations.
“Making a positive impact” calls for a transformation in how we live, work, and cooperate globally. As individuals, communities, businesses, and nations, we hold the keys to unlocking a sustainable and resilient future. By embracing innovation, fostering adaptive capacities, and prioritizing sustainability, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and safeguard our planet for future generations.
Sources
NOAA National Centers for Environmental information, Climate at a Glance: Global Time Series, published February 2024, retrieved on February 28, 2024 from https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/climate-at-a-glance/global/time-series

